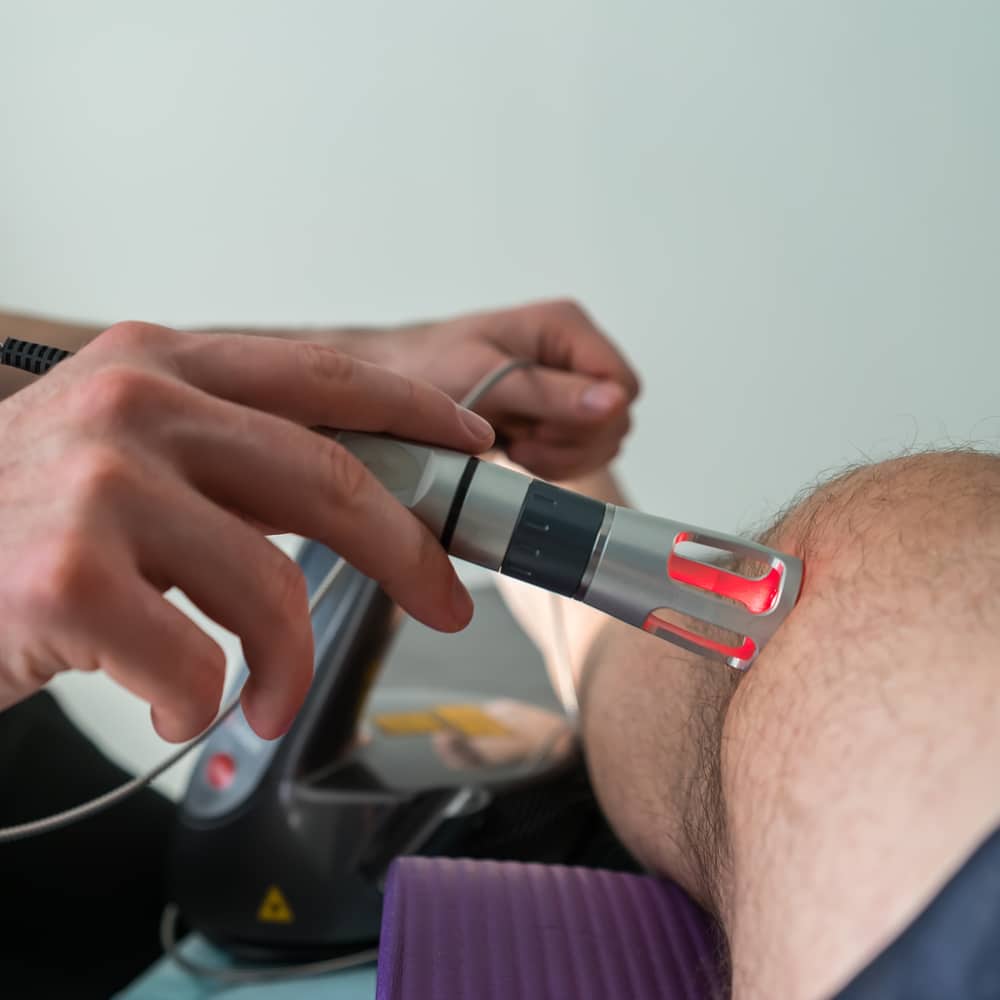
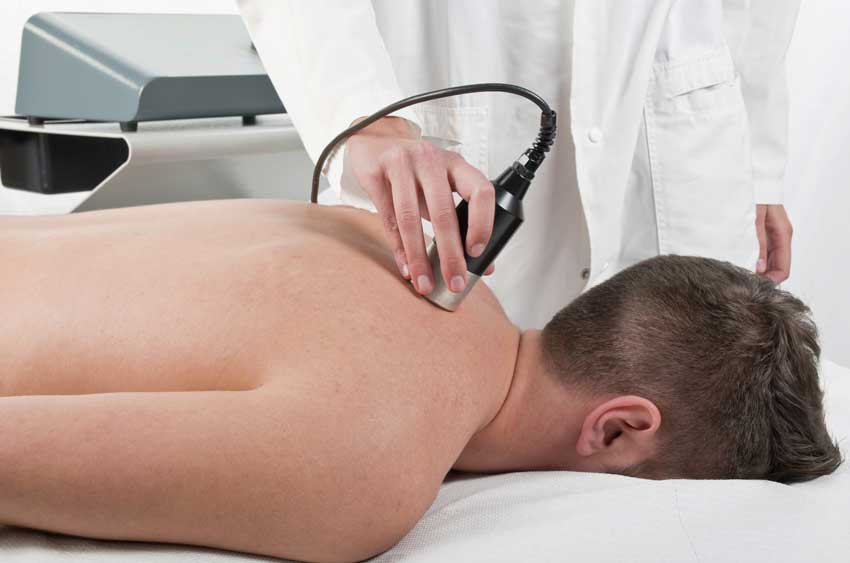
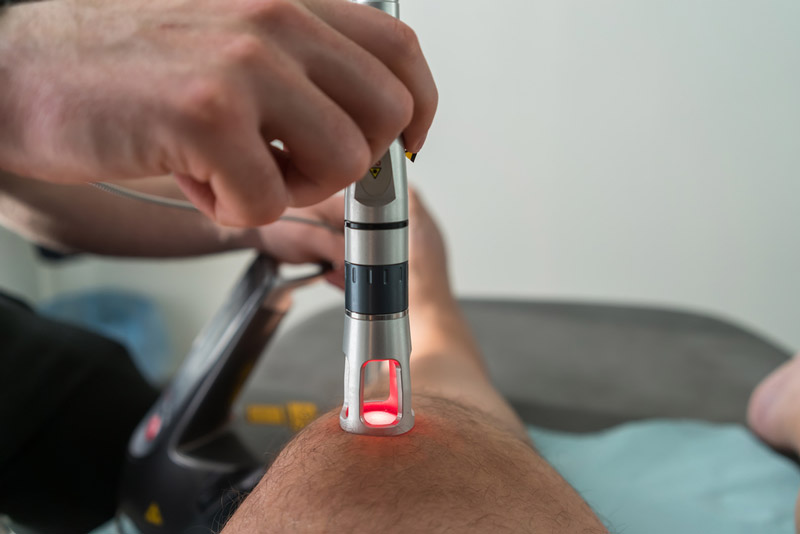
Temporomandibular Dysfunction and the Cranio-Cervico-Pelvic Axis: A Neurofunctional Integrative Perspective
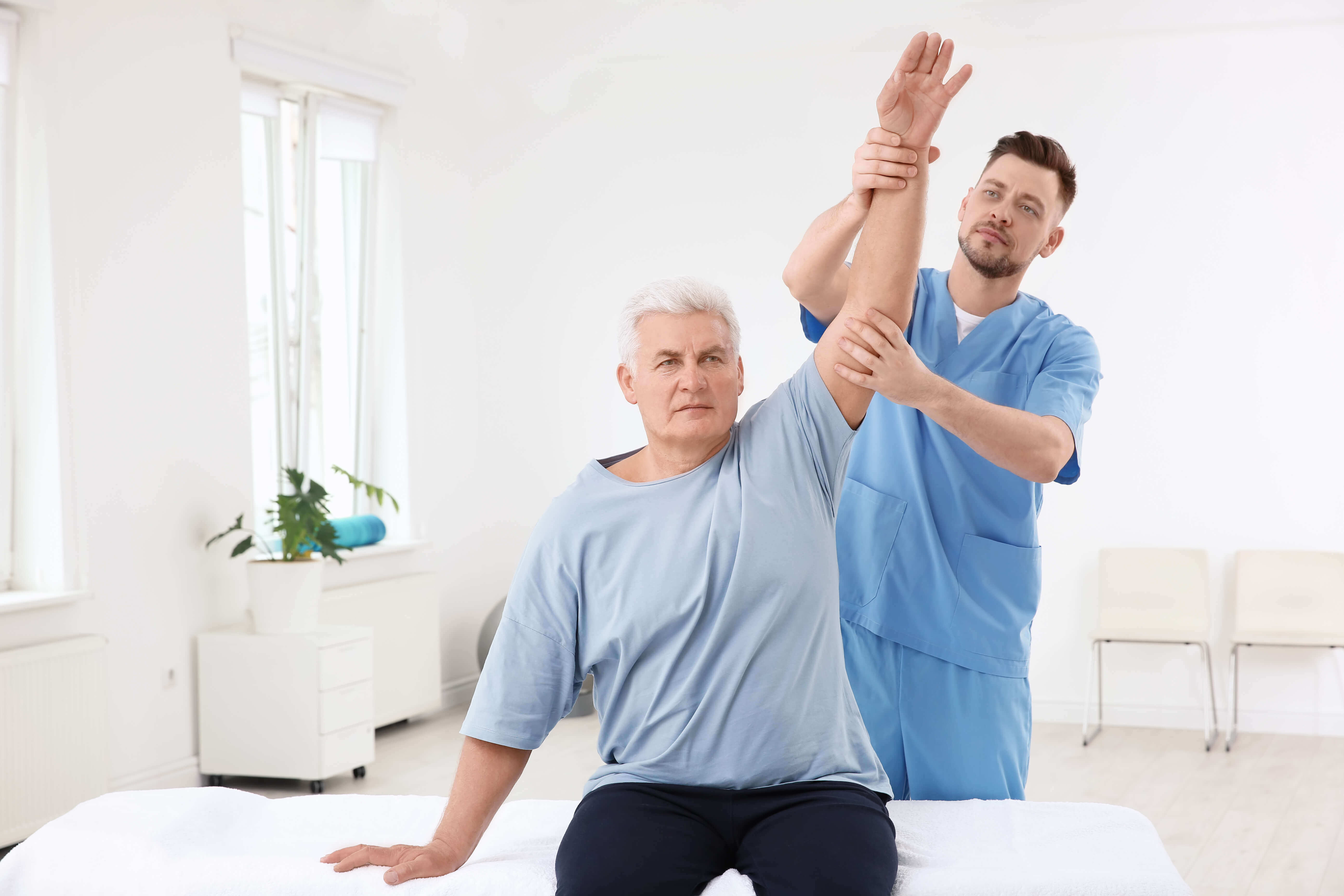
🧠 Temporomandibular Dysfunction and the Cranio-Cervico-Pelvic Axis: A Neurofunctional Integrative Perspective Temporomandibular disorders (TMD) have historically been approached from a dental perspective, focusing on occlusion, dental alignment, and splint therapy. However, recent decades have witnessed a paradigm shift driven by advances in pain neuroscience, functional biomechanics, and physical medicine. This new paradigm recognizes the temporomandibular …